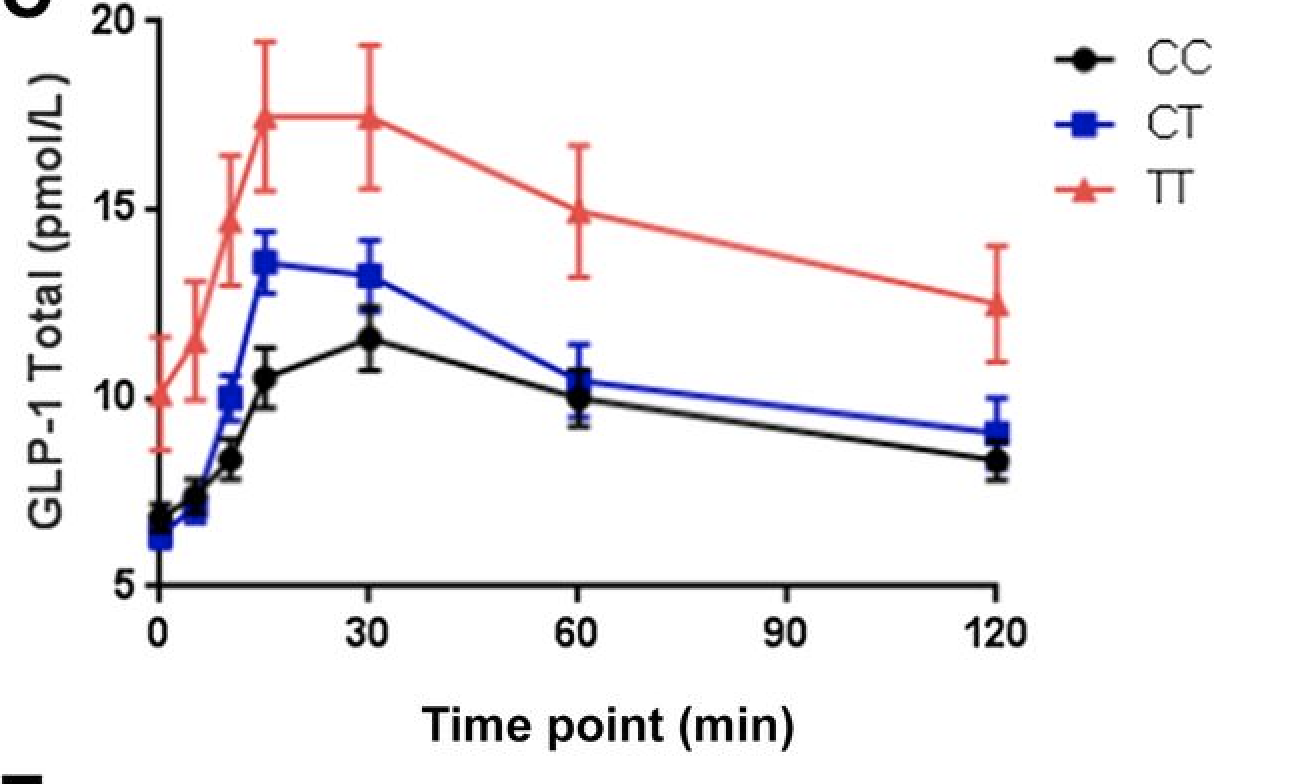
TCF7L2 Genetic Variation Augments Incretin Resistance and Influences Response to a Sulfonylurea and Metformin: The Study to Understand the Genetics of the Acute Response to Metformin and Glipizide in Humans (SUGAR-MGH)
OBJECTIVE The rs7903146 T allele in transcription factor 7 like 2 (TCF7L2) is strongly associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D), but the mechanisms for increased risk remain unclear. We evaluated the physiologic and hormonal effects of TCF7L2 genotype before and after interventions that influence glucose physiology. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS We genotyped rs7903146 in 608 …
Variation in Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young genes influence response to interventions for diabetes prevention
CONTEXT: Variation in genes that cause Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) has been associated with diabetes incidence and glycemic traits. OBJECTIVES: This study aimed to determine whether genetic variation in MODY genes leads to differential responses to insulin-sensitizing interventions. DESIGN AND SETTING: This was a secondary analysis of a multicenter randomized clinical trial, the …
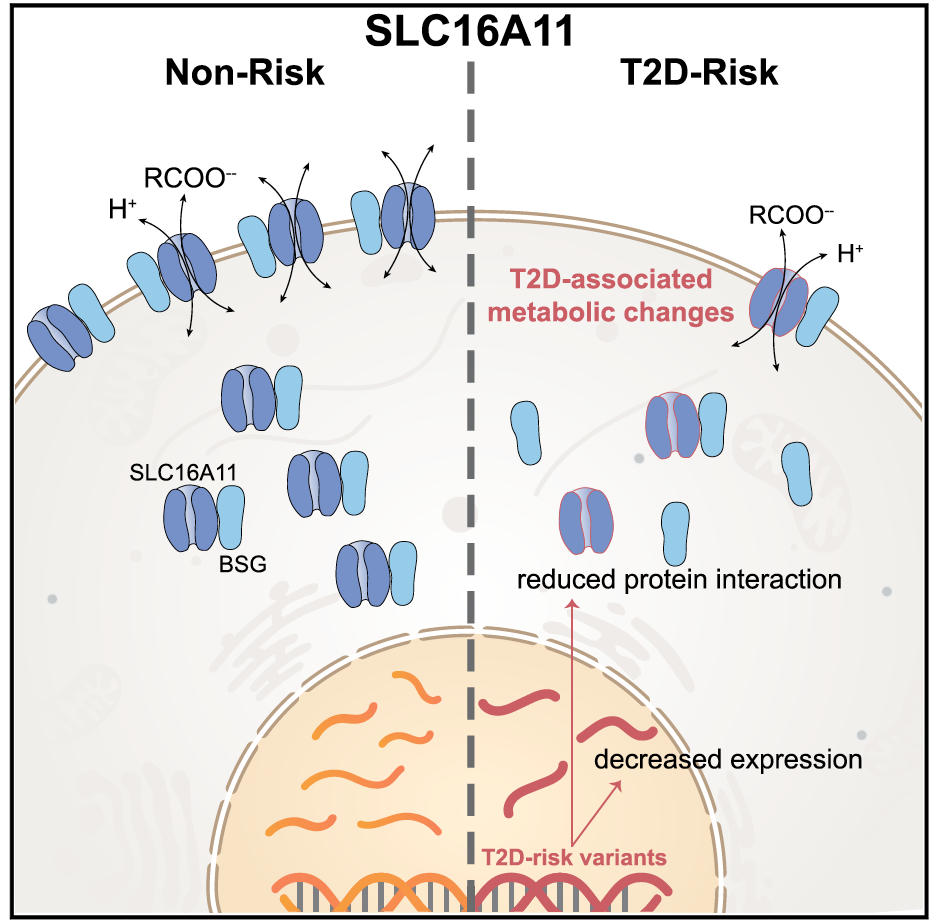
Type 2 diabetes variants disrupt function of SLC16A11 through two distinct mechanisms
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) affects Latinos at twice the rate seen in populations of European descent. We recently identified a risk haplotype spanning SLC16A11 that explains ?20% of the increased T2D prevalence in Mexico. Here, through genetic fine-mapping, we define a set of tightly linked variants likely to contain the causal allele(s). We show that …
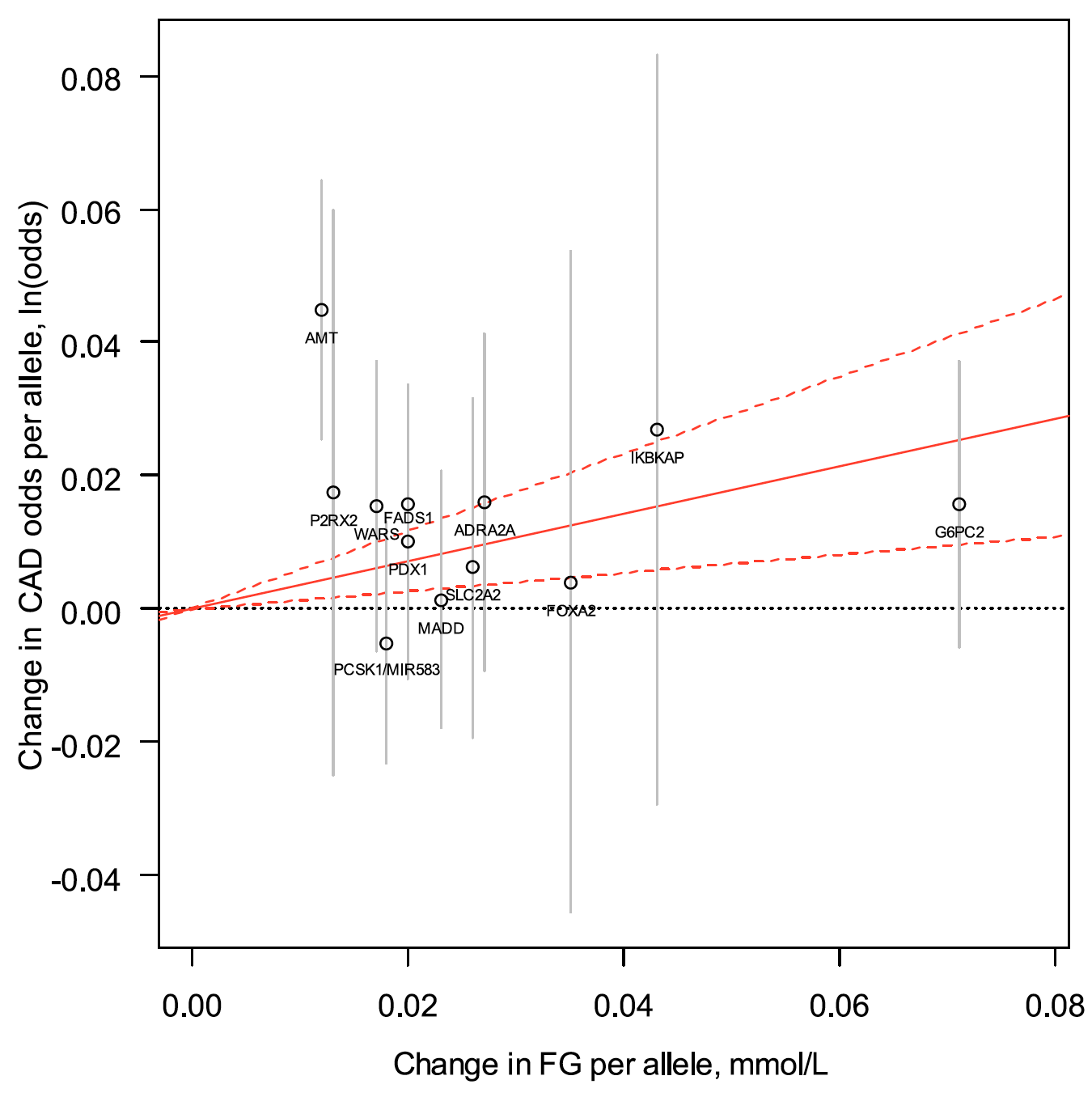
Genetically driven hyperglycemia increases risk of coronary artery disease separately from type 2 diabetes
OBJECTIVE: This study tested the hypothesis that genetically raised hyperglycemia increases coronary artery disease (CAD) risk separately from the risk conferred by type 2 diabetes as a whole. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS: We conducted a Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis using summary-level statistics from the largest published meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for fasting glucose …
Genome-wide association study of the modified Stumvoll Insulin Sensitivity Index identifies BCL2 and FAM19A2 as novel insulin sensitivity loci
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have found few common variants that influence fasting measures of insulin sensitivity. We hypothesized that a GWAS of an integrated assessment of fasting and dynamic measures of insulin sensitivity would detect novel common variants. We performed a GWAS of the modified Stumvoll Insulin Sensitivity Index (ISI) within the Meta-Analyses of Glucose …
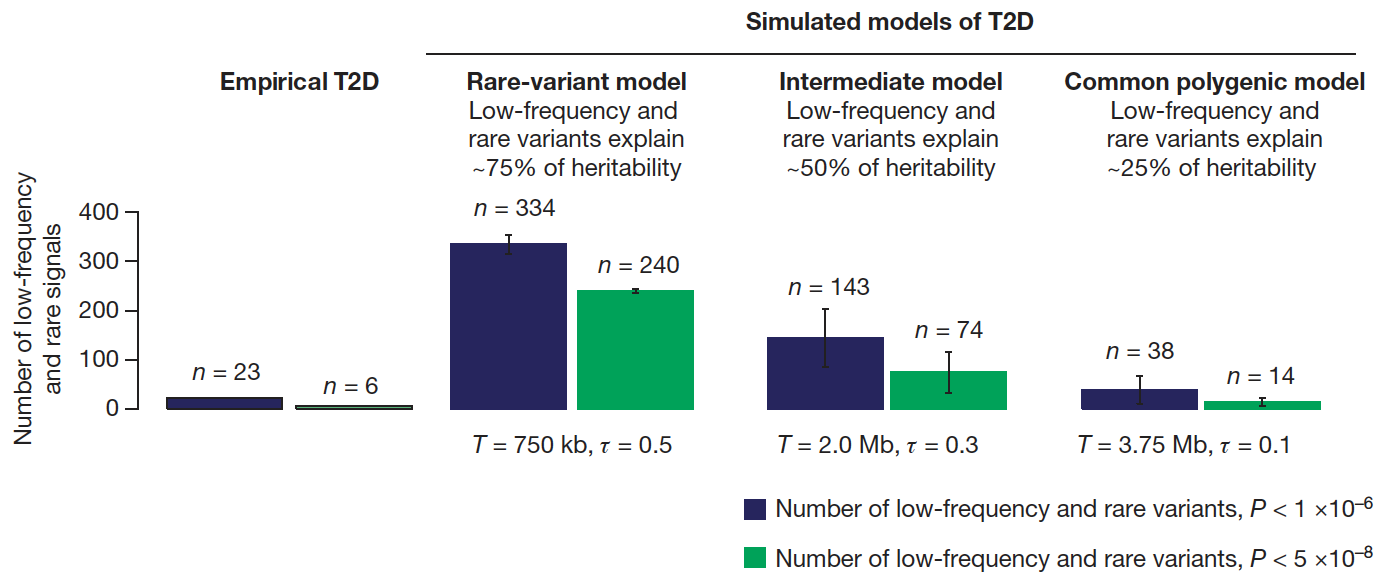
The genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes
The genetic architecture of common traits, including the number, frequency, and effect sizes of inherited variants that contribute to individual risk, has been long debated. Genome-wide association studies have identified scores of common variants associated with type 2 diabetes, but in aggregate, these explain only a fraction of the heritability of this disease. Here, to …
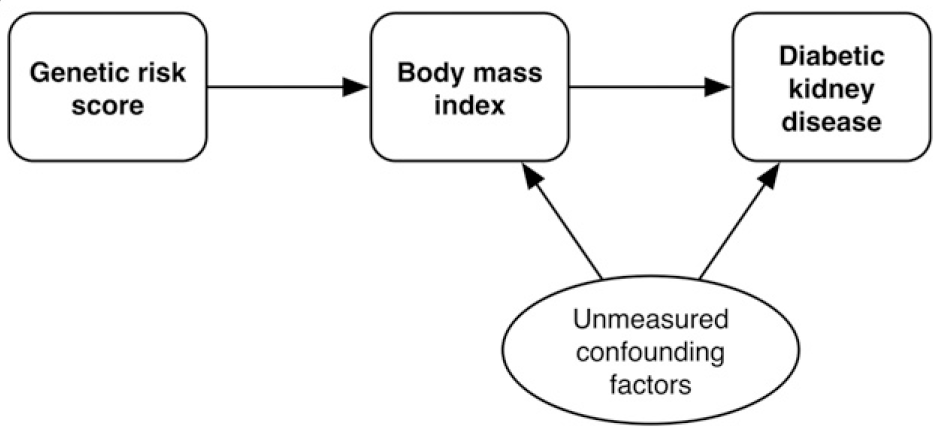
Genetic evidence for a causal role of obesity in diabetic kidney disease
Obesity has been posited as an independent risk factor for diabetic kidney disease (DKD), but establishing causality from observational data is problematic. We aimed to test whether obesity is causally related to DKD using Mendelian randomization, which exploits the random assortment of genes during meiosis. In 6,049 subjects with type 1 diabetes, we used a …
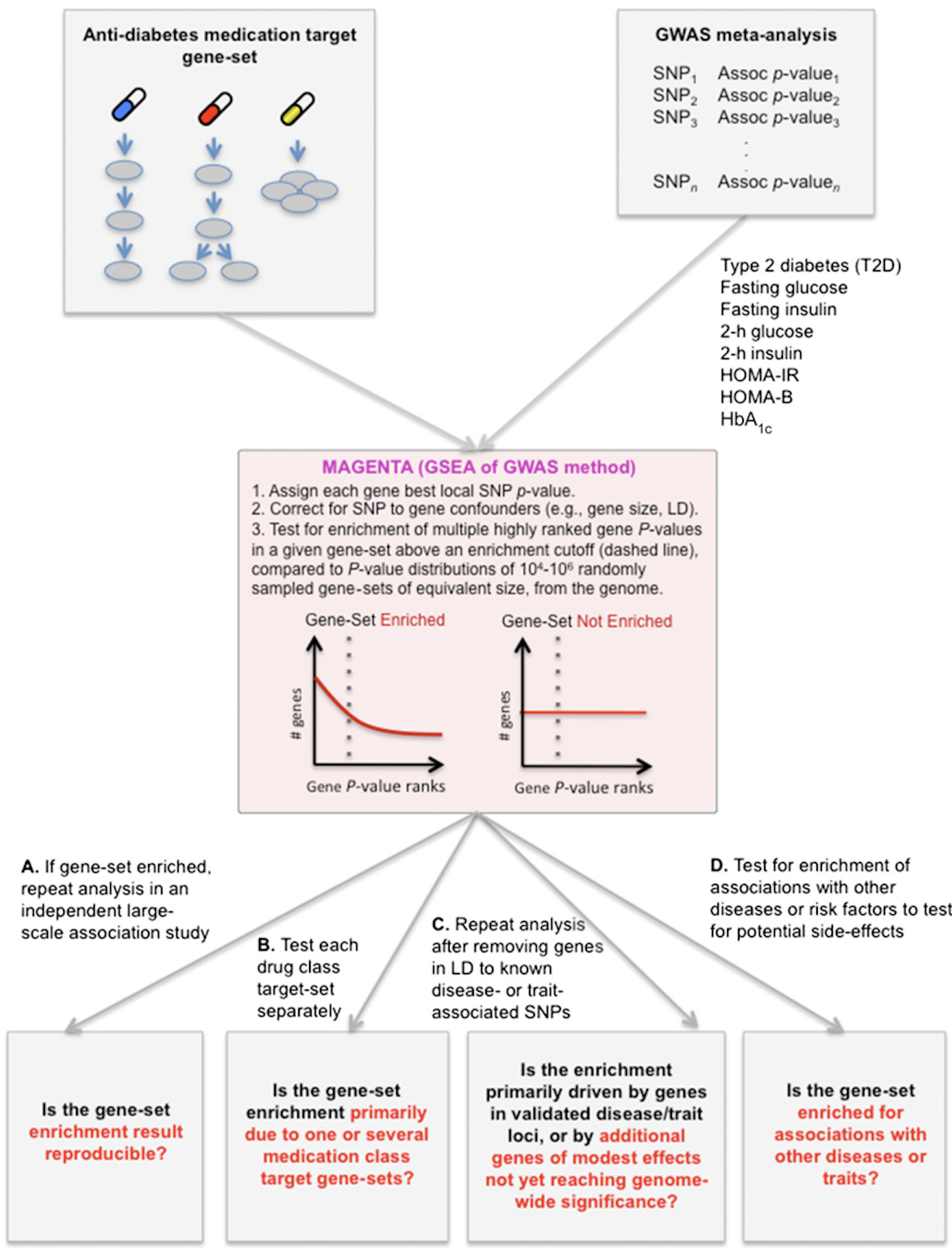
Pathways targeted by anti-diabetes drugs are enriched for multiple genes associated with type 2 diabetes risk
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have uncovered >65 common variants associated with type 2 diabetes (T2D); however, their relevance for drug development is not yet clear. Of note, the first two T2D-associated loci (PPARG and KCNJ11/ABCC8) encode known targets of antidiabetes medications. We therefore tested whether other genes/pathways targeted by antidiabetes drugs are associated with T2D. …
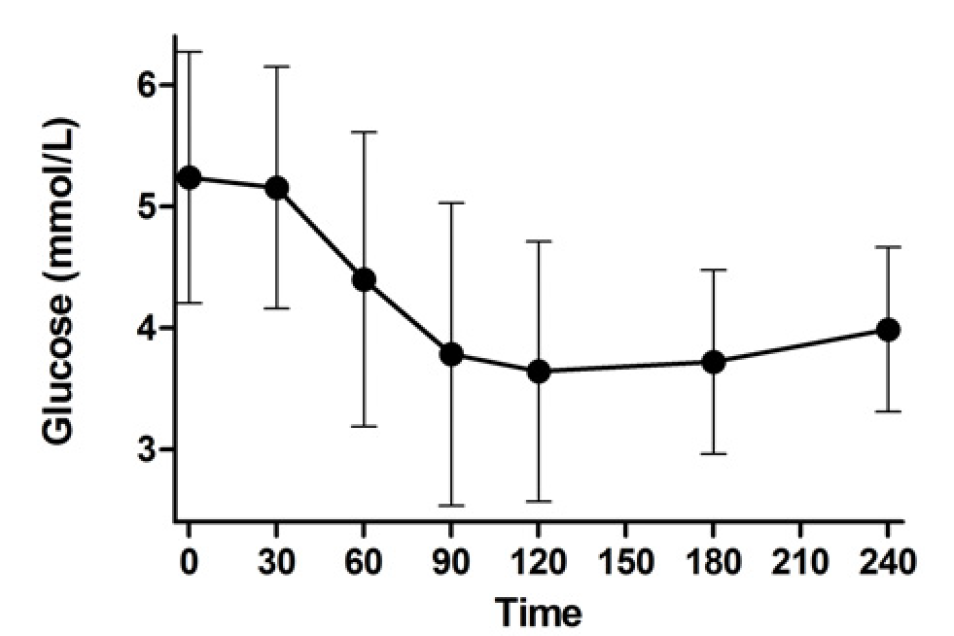
The Study to Understand the Genetics of the Acute Response to Metformin and Glipizide in Humans (SUGAR-MGH): Design of a pharmacogenetic resource for type 2 diabetes
OBJECTIVE: Genome-wide association studies have uncovered a large number of genetic variants associated with type 2 diabetes or related phenotypes. In many cases the causal gene or polymorphism has not been identified, and its impact on response to anti-hyperglycemic medications is unknown. The Study to Understand the Genetics of the Acute Response to Metformin and …
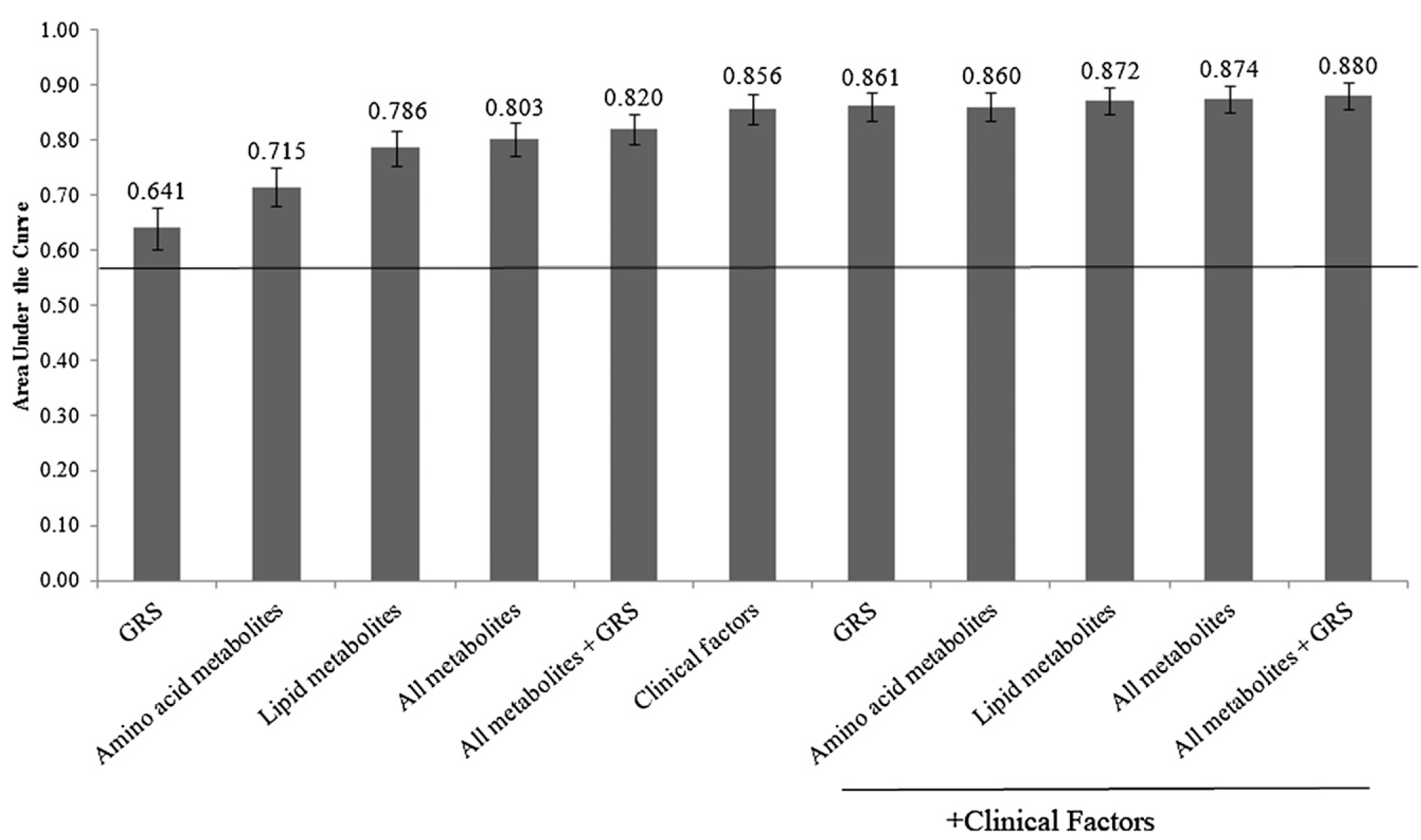
Metabolite Traits and Genetic Risk Provide Complementary Information for the Prediction of Future Type 2 Diabetes
OBJECTIVE A genetic risk score (GRS) comprised of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) andmetabolite biomarkers have each been shown, separately, to predict incident type 2 diabetes. We tested whether genetic and metabolite markers provide complementary information for type 2 diabetes prediction and, together, improve the accuracy of prediction models containing clinical traits. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS …



