Mining the genome for therapeutic targets
Current pharmacological options for type 2 diabetes do not cure the disease. Despite the availability of multiple drug classes that modulate glycemia effectively and minimize long-term complications, these agents do not reverse pathogenesis, and in practice they are not selected to correct the molecular profile specific to the patient. Pharmaceutical companies find drug development programs …
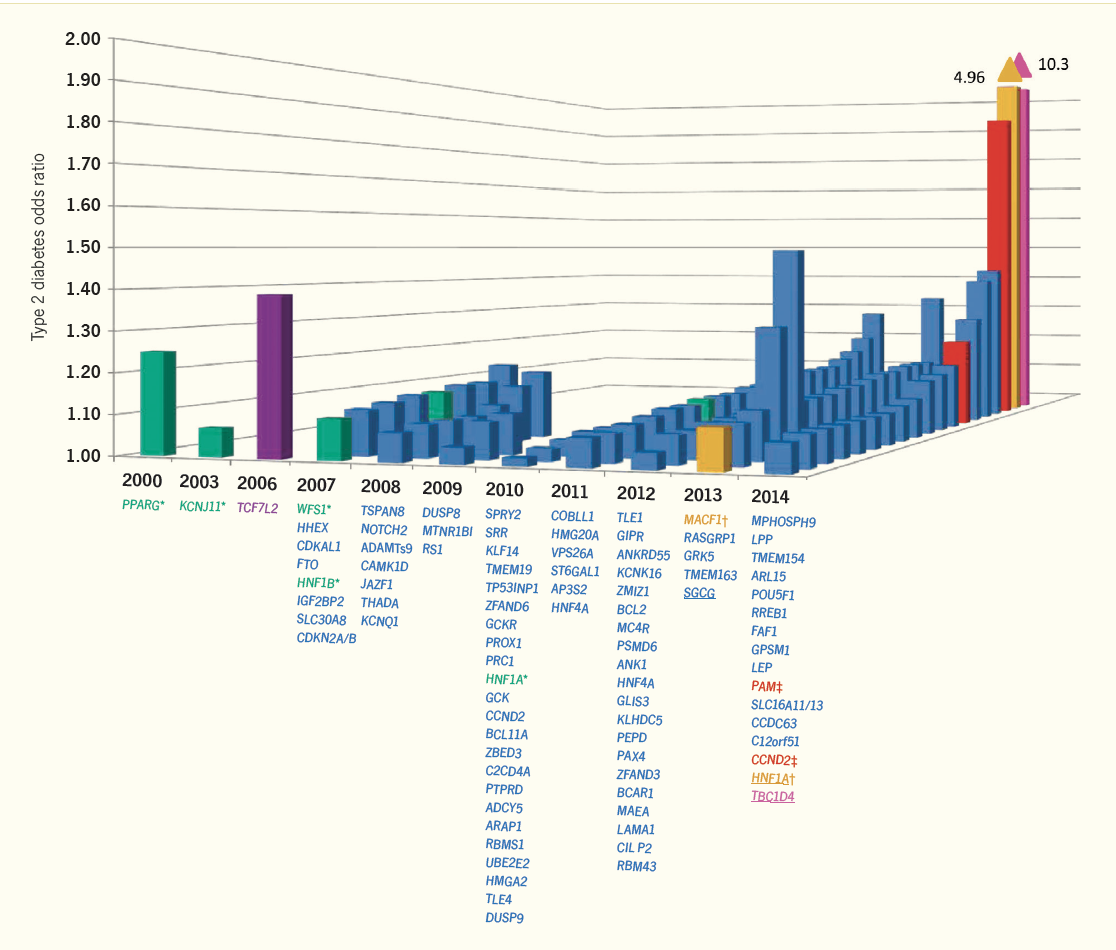
Genetics of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is thought to result from a combination of environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors, with the heritability of type 2 diabetes estimated to be in the range of 25% to 72% based on family and twin studies. Since early 2007, genomewide association studies (GWAS) have led to an explosion of data for the …

Pharmacogenetics in type 2 diabetes: precision medicine or discovery tool?
In recent years, technological and analytical advances have led to an explosion in the discovery of genetic loci associated with type 2 diabetes. However, their ability to improve prediction of disease outcomes beyond standard clinical risk factors has been limited. On the other hand, genetic effects on drug response may be stronger than those commonly …
The pharmacogenetics of metformin
Despite its widespread use as the first-line agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, it has become clear that metformin does not work optimally for everyone. Elucidating who are the likely metformin responders and non-responders is hampered by our limited knowledge of its precise molecular mechanism of action. One approach to achieve the related …
Leveraging genetics to advance type 2 diabetes prevention
In this Perspective, Jose Florez discusses how information from genetics and genomics may be able to contribute to prevention of type 2 diabetes and predicting individual responses to behavioral and other interventions. …
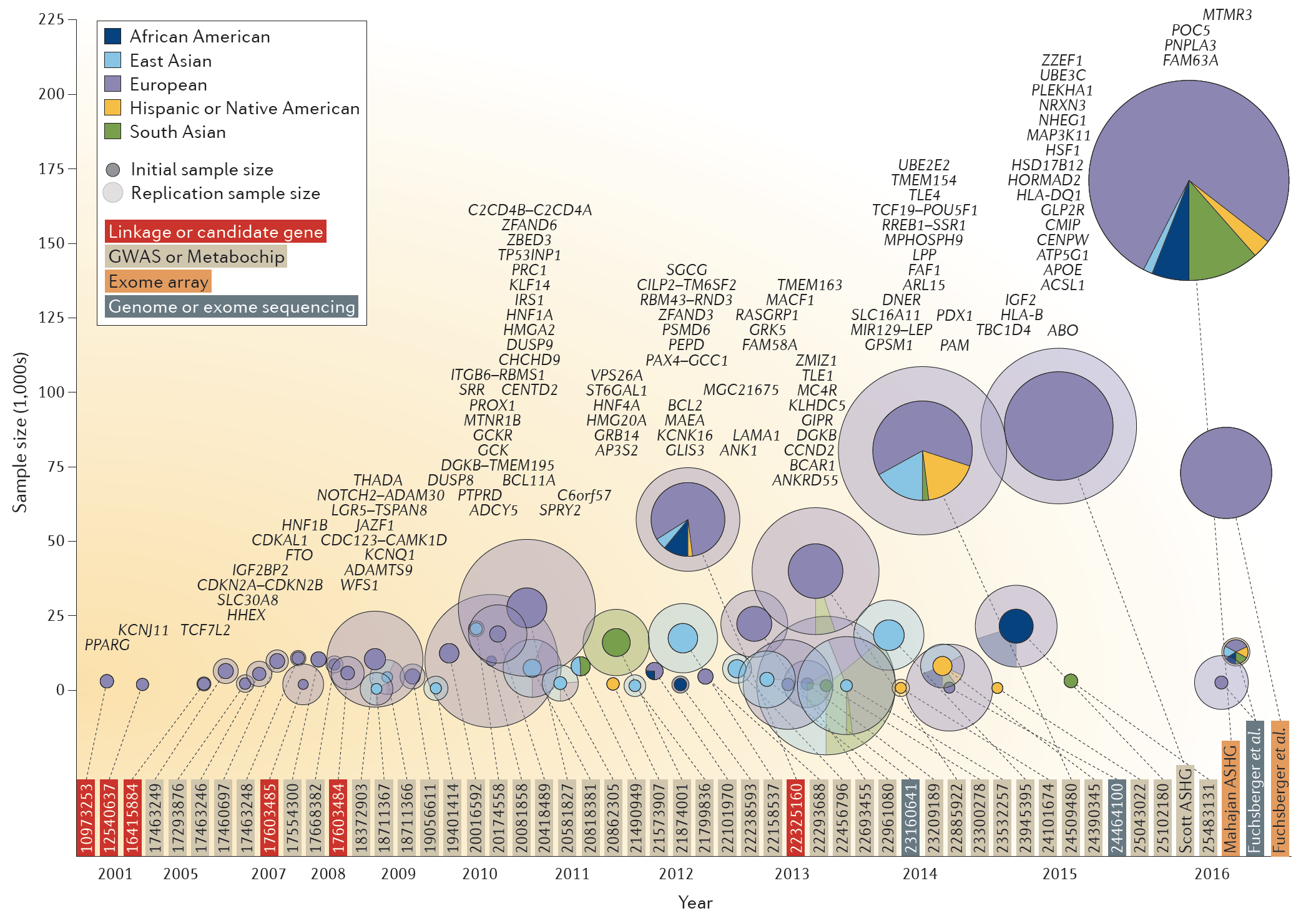
Type 2 diabetes: genetic data sharing to advance complex disease research
As with other complex diseases, unbiased association studies followed by physiological and experimental characterization have for years formed a paradigm for identifying genes or processes of relevance to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Recent large-scale common and rare variant genome-wide association studies (GWAS) suggest that substantially larger association studies are needed to identify most T2D …

Therapeutic challenges in diabetes prevention: We have not found the “exercise pillâ€
Type 2 diabetes has become an enormous public health burden, making diabetes prevention a pressing issue. While lifestyle modification is the most effective preventive strategy, it is resource-intensive and not universally sustainable. We review the evidence on pharmacological options for diabetes prevention, in search of a medication that is efficacious, easy to adhere to, well …
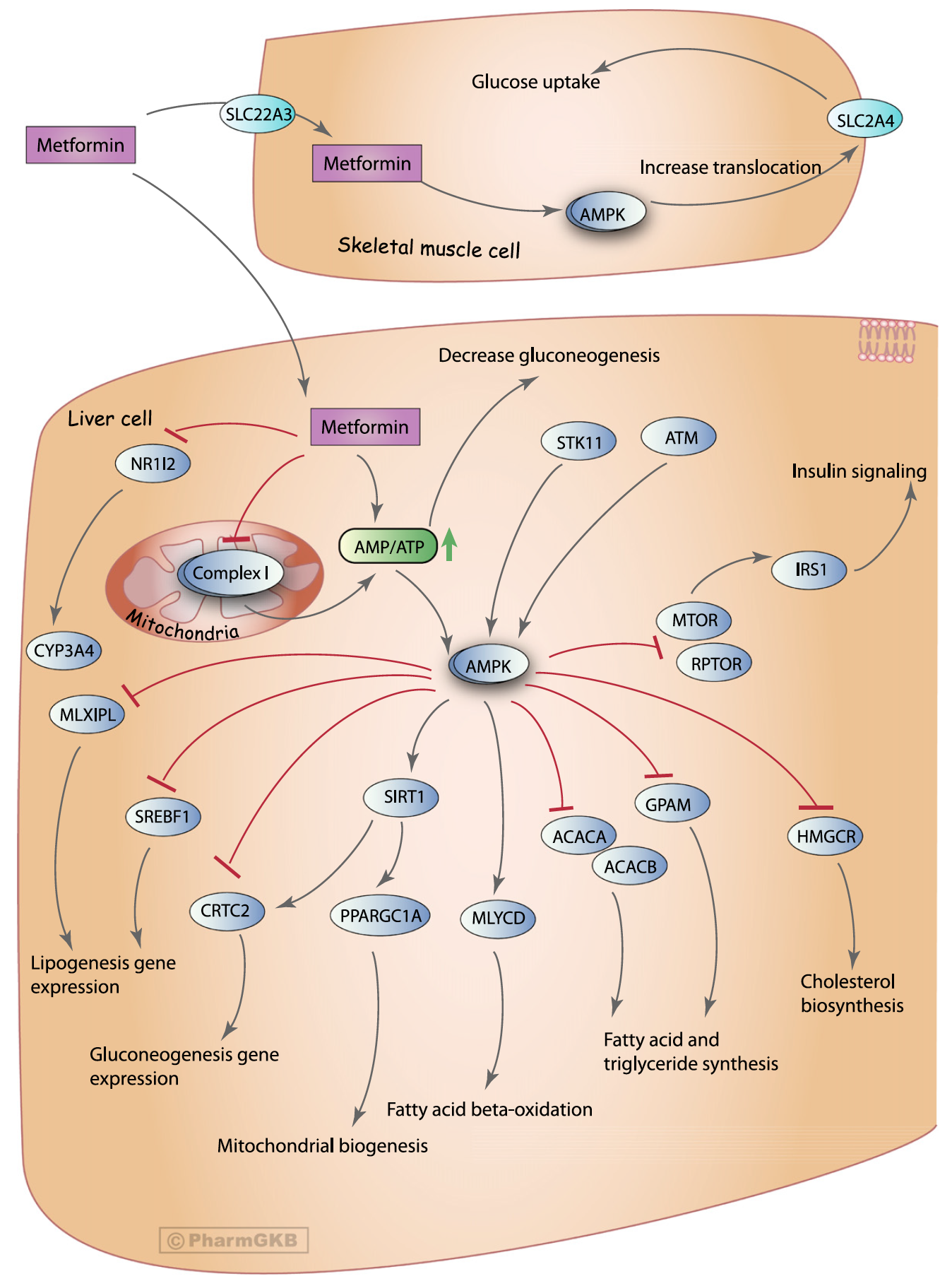
Metformin pharmacogenomics: current status and future directions
The incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and its costs to the health care system continue to rise. Despite the availability of at least 10 drug classes for the treatment of T2D, metformin remains the most widely used first-line pharmacotherapy for its treatment; however, marked interindividual variability in response and few clinical or biomarker predictors …
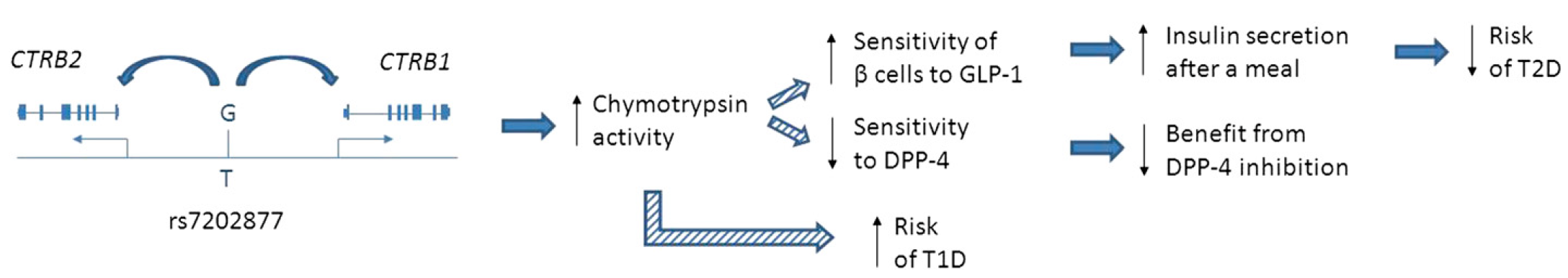
Pharmacogenetic perturbations in humans as a tool to generate mechanistic insight
…



